fstat obtains information about the open file associated with the given handle and stores it in the structure to which buffer points. The <sys\stat.h> include file defines the stat structure. The stat structure contains the following fields:
Field
- Value
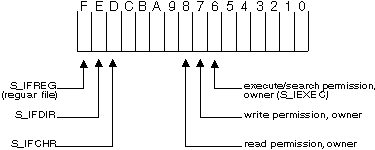
- Bit mask for file mode information. fstat sets
the S_IFCHR bit if handle refers to a device. The S_IFDIR bit is
set if pathname specifies a directory. It sets the S_IFREG bit if
handle refers to an ordinary file. It sets user read/write bits
according to the permission mode of the file. The other bits have undefined
values.
st_dev
- Drive number of the disk containing the
file.
- Drive number
of the disk containing the file (same as st_dev).
- Always 1.
- Size
of the file in bytes.
- Time
of last access of file.
- Time
of last modification of file.
- Time
of file creation.
There are three additional fields in the stat structure for portability to other operating systems; they have no meaning under the OS/2 operating system.
Note: If the given handle refers to a device, the size and time fields in the stat structure are not meaningful.